728x90
들어가며
포스팅된 글은 아래에 첨부된 논문과 유튜브 영상을 바탕으로 공부를 한 내용입니다.
이외에도 구글링을 통해 다양한 글들을 참고하며 공부한 내용을 포스팅 한 것 입니다.
또한 본 프로젝트는 클론코딩을 기반으로 공부한 것 입니다.
더보기
논문 제목: Image Style Transfer Using Convolutional Neural Networks (CVPR 2016)
논문 링크: https://rn-unison.github.io/articulos/style_transfer.pdf
이전 프로젝트 과정
1. Image Reconstruction 실습 | Image Style Transfer Using Convolutional Neural Networks (CVPR 2016)
들어가며 포스팅된 글은 아래에 첨부된 논문과 유튜브 영상을 바탕으로 공부를 한 내용입니다. 이외에도 구글링을 통해 다양한 글들을 참고하며 공부한 내용을 포스팅 한 것 입니다. 또한 본 프
all-young.tistory.com
프로젝트 과정
실습을 위한 이미지 불러오기
In [8]:
# 콘텐츠(Content) 이미지와 스타일(Style) 이미지를 모두 준비합니다.
content_img = image_loader('./code_practices/images/content_img_1.jpg', (512, 640))
style_img = image_loader('./code_practices/images/style_img_1.jpg', (512, 640))
print("[ Content Image ]")
imshow(content_img)
print("[ Style Image ]")
imshow(style_img)
[ Content Image ]

[ Style Image ]

CNN 네트워크 불러오기
In [9]:
# 뉴럴 네트워크 모델을 불러옵니다.
cnn = models.vgg19(pretrained=True).features.to(device).eval()
print(cnn)
Downloading: "https://download.pytorch.org/models/vgg19-dcbb9e9d.pth" to C:\Users\Jung_dayoung/.cache\torch\hub\checkpoints\vgg19-dcbb9e9d.pth
Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(1): ReLU(inplace=True)
(2): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(3): ReLU(inplace=True)
(4): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(5): Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(6): ReLU(inplace=True)
(7): Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(8): ReLU(inplace=True)
(9): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(10): Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(11): ReLU(inplace=True)
(12): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(13): ReLU(inplace=True)
(14): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(15): ReLU(inplace=True)
(16): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(17): ReLU(inplace=True)
(18): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(19): Conv2d(256, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(20): ReLU(inplace=True)
(21): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(22): ReLU(inplace=True)
(23): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(24): ReLU(inplace=True)
(25): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(26): ReLU(inplace=True)
(27): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(28): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(29): ReLU(inplace=True)
(30): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(31): ReLU(inplace=True)
(32): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(33): ReLU(inplace=True)
(34): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(35): ReLU(inplace=True)
(36): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
In [10]:
# 입력 정규화(Normalization)를 위한 초기화
cnn_normalization_mean = torch.tensor([0.485, 0.456, 0.406]).to(device)
cnn_normalization_std = torch.tensor([0.229, 0.224, 0.225]).to(device)
class Normalization(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, mean, std):
super(Normalization, self).__init__()
self.mean = mean.clone().view(-1, 1, 1)
self.std = std.clone().view(-1, 1, 1)
def forward(self, img):
return (img - self.mean) / self.std
Style Reconstruction 실습하기
In [11]:
def gram_matrix(input):
# a는 배치 크기, b는 특징 맵의 개수, (c, d)는 특징 맵의 차원을 의미
a, b, c, d = input.size()
# 논문에서는 i = 특징 맵의 개수, j = 각 위치(position)
features = input.view(a * b, c * d)
# 행렬 곱으로 한 번에 Gram 내적 계산 가능
G = torch.mm(features, features.t())
# Normalize 목적으로 값 나누기
return G.div(a * b * c * d)
# 스타일 손실(style loss) 계산을 위한 클래스 정의
class StyleLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, target_feature):
super(StyleLoss, self).__init__()
self.target = gram_matrix(target_feature).detach()
def forward(self, input):
G = gram_matrix(input)
self.loss = F.mse_loss(G, self.target)
return input
In [12]:
style_layers = ['conv_1', 'conv_2', 'conv_3', 'conv_4', 'conv_5']
# 스타일 손실(style loss)을 계산하는 함수
def get_style_losses(cnn, style_img, noise_image):
cnn = copy.deepcopy(cnn)
normalization = Normalization(cnn_normalization_mean, cnn_normalization_std).to(device)
style_losses = []
# 가장 먼저 입력 이미지가 입력 정규화(input normalization)를 수행하도록
model = nn.Sequential(normalization)
# 현재 CNN 모델에 포함되어 있는 모든 레이어를 확인하며
i = 0
for layer in cnn.children():
if isinstance(layer, nn.Conv2d):
i += 1
name = 'conv_{}'.format(i)
elif isinstance(layer, nn.ReLU):
name = 'relu_{}'.format(i)
layer = nn.ReLU(inplace=False)
elif isinstance(layer, nn.MaxPool2d):
name = 'pool_{}'.format(i)
elif isinstance(layer, nn.BatchNorm2d):
name = 'bn_{}'.format(i)
else:
raise RuntimeError('Unrecognized layer: {}'.format(layer.__class__.__name__))
model.add_module(name, layer)
# 설정한 style layer까지의 결과를 이용해 style loss를 계산
if name in style_layers:
target_feature = model(style_img).detach()
style_loss = StyleLoss(target_feature)
model.add_module("style_loss_{}".format(i), style_loss)
style_losses.append(style_loss)
# 마지막 style loss 이후의 레이어는 사용하지 않도록
for i in range(len(model) - 1, -1, -1):
if isinstance(model[i], StyleLoss):
break
model = model[:(i + 1)]
return model, style_losses
In [13]:
def style_reconstruction(cnn, style_img, input_img, iters):
model, style_losses = get_style_losses(cnn, style_img, input_img)
optimizer = optim.LBFGS([input_img.requires_grad_()])
print("[ Start ]")
imshow(input_img)
# 하나의 값만 이용하기 위해 배열 형태로 사용
run = [0]
while run[0] <= iters:
def closure():
input_img.data.clamp_(0, 1)
optimizer.zero_grad()
model(input_img)
style_score = 0
for sl in style_losses:
style_score += sl.loss
style_score *= 1e6
style_score.backward()
run[0] += 1
if run[0] % 50 == 0:
print(f"[ Step: {run[0]} / Style loss: {style_score.item()}]")
imshow(input_img)
return style_score
optimizer.step(closure)
# 결과적으로 이미지의 각 픽셀의 값이 [0, 1] 사이의 값이 되도록 자르기
input_img.data.clamp_(0, 1)
return input_img
In [14]:
# 콘텐츠 이미지와 동일한 크기의 노이즈 이미지 준비하기
input_img = torch.empty_like(content_img).uniform_(0, 1).to(device)
imshow(input_img)

In [15]:
# style reconstruction 수행
output = style_reconstruction(cnn, style_img=style_img, input_img=input_img, iters=300)
[ Start ]

[ Step: 50 / Style loss: 401.36480712890625]
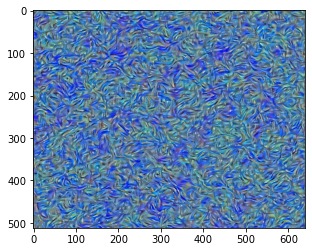
[ Step: 100 / Style loss: 98.27745056152344]

[ Step: 150 / Style loss: 48.27903366088867]

[ Step: 200 / Style loss: 35.383583068847656]

[ Step: 250 / Style loss: 28.44278907775879]
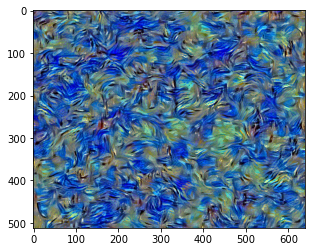
[ Step: 300 / Style loss: 23.4752197265625]
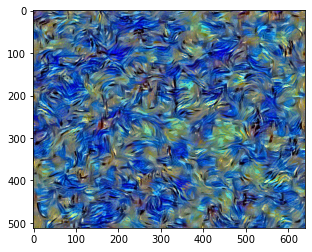
Content Reconstruction 실습하기
In [16]:
# 콘텐츠 손실(content loss) 계산을 위한 클래스 정의
class ContentLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, target,):
super(ContentLoss, self).__init__()
self.target = target.detach()
def forward(self, input):
self.loss = F.mse_loss(input, self.target)
return input
In [17]:
content_layers = ['conv_4']
# 콘텐츠 손실(content loss)을 계산하는 함수
def get_content_losses(cnn, content_img, noise_image):
cnn = copy.deepcopy(cnn)
normalization = Normalization(cnn_normalization_mean, cnn_normalization_std).to(device)
content_losses = []
# 가장 먼저 입력 이미지가 입력 정규화(input normalization)를 수행하도록
model = nn.Sequential(normalization)
# 현재 CNN 모델에 포함되어 있는 모든 레이어를 확인하며
i = 0
for layer in cnn.children():
if isinstance(layer, nn.Conv2d):
i += 1
name = 'conv_{}'.format(i)
elif isinstance(layer, nn.ReLU):
name = 'relu_{}'.format(i)
layer = nn.ReLU(inplace=False)
elif isinstance(layer, nn.MaxPool2d):
name = 'pool_{}'.format(i)
elif isinstance(layer, nn.BatchNorm2d):
name = 'bn_{}'.format(i)
else:
raise RuntimeError('Unrecognized layer: {}'.format(layer.__class__.__name__))
model.add_module(name, layer)
# 설정한 content layer까지의 결과를 이용해 content loss를 계산
if name in content_layers:
target_feature = model(content_img).detach()
content_loss = ContentLoss(target_feature)
model.add_module("content_loss_{}".format(i), content_loss)
content_losses.append(content_loss)
# 마지막 content loss 이후의 레이어는 사용하지 않도록
for i in range(len(model) - 1, -1, -1):
if isinstance(model[i], ContentLoss):
break
model = model[:(i + 1)]
return model, content_losses
In [18]:
def content_reconstruction(cnn, content_img, input_img, iters):
model, content_losses = get_content_losses(cnn, content_img, input_img)
optimizer = optim.LBFGS([input_img.requires_grad_()])
print("[ Start ]")
imshow(input_img)
# 하나의 값만 이용하기 위해 배열 형태로 사용
run = [0]
while run[0] <= iters:
def closure():
input_img.data.clamp_(0, 1)
optimizer.zero_grad()
model(input_img)
content_score = 0
for cl in content_losses:
content_score += cl.loss
content_score.backward()
run[0] += 1
if run[0] % 50 == 0:
print(f"[ Step: {run[0]} / Content loss: {content_score.item()}]")
imshow(input_img)
return content_score
optimizer.step(closure)
# 결과적으로 이미지의 각 픽셀의 값이 [0, 1] 사이의 값이 되도록 자르기
input_img.data.clamp_(0, 1)
return input_img
In [19]:
# 콘텐츠 이미지와 동일한 크기의 노이즈 이미지 준비하기
input_img = torch.empty_like(content_img).uniform_(0, 1).to(device)
imshow(input_img)

In [20]:
# content reconstruction 수행
output = content_reconstruction(cnn, content_img=content_img, input_img=input_img, iters=300)
[ Start ]

[ Step: 50 / Content loss: 0.7528634071350098]

[ Step: 100 / Content loss: 0.37445318698883057]

[ Step: 150 / Content loss: 0.24265167117118835]

[ Step: 200 / Content loss: 0.1740923374891281]

[ Step: 250 / Content loss: 0.13262364268302917]

[ Step: 300 / Content loss: 0.10329753160476685]

다음 프로젝트 과정
3. Style Transfer 실습 | Image Style Transfer Using Convolutional Neural Networks (CVPR 2016)
들어가며 포스팅된 글은 아래에 첨부된 논문과 유튜브 영상을 바탕으로 공부를 한 내용입니다. 이외에도 구글링을 통해 다양한 글들을 참고하며 공부한 내용을 포스팅 한 것 입니다. 또한 본 프
all-young.tistory.com



